Can you legally use your private car or bike for deliveries, or is commercial registration required? This is one of the most common questions asked by delivery partners, small business owners, and first-time logistics operators in India. The difference between private vehicle registration vs commercial vehicle registration is not just about number plate colour; it directly affects legality, insurance validity, fines, and long-term business safety.
In 2026, with the rapid growth of last-mile delivery, electric bikes, and logistics fleets, enforcement around vehicle usage has become stricter. Many people unknowingly use white-plate vehicles for delivery work and face challans, permit issues, or rejected insurance claims. Platforms like MOVER, which rely on compliant vehicles for seamless logistics operations, underscore the importance of accurate registration from the outset.
This guide explains the real difference between private and commercial vehicle registration in India, including number plates, insurance, permits, and delivery usage, so you can choose the right option without legal or financial risk.
What Is Private Vehicle Registration?
Private vehicle registration is meant strictly for personal use. Vehicles registered under this category are allowed for daily commuting, family travel, and non-commercial activities only. These vehicles cannot legally be used to earn money through deliveries, transport, or passenger services.
In India, private vehicles carry white number plates with black lettering, making them easy to identify during checks. The rules for private registration are simpler, with lower road tax, fewer compliance requirements, and no need for fitness certificates or commercial permits. A standard private driving licence is sufficient to operate these vehicles.
Private vehicles must be covered under private motor insurance, which only protects personal use. If a private vehicle is used for delivery or logistics work, the insurance becomes invalid, and any accident claim may be rejected. This is why private registration is suitable only for personal travel, not for delivery or business use.
What Is Commercial Vehicle Registration?
Commercial vehicle registration applies to any vehicle used for business or income-generating purposes, including delivery bikes, courier vans, goods carriers, and logistics vehicles. These vehicles must carry yellow number plates and comply with permit, fitness, road tax, and commercial insurance rules.
In 2026, correct commercial registration is mandatory for delivery operations to function without disruption. Vehicles operating through platforms like MOVER must meet registration and insurance requirements to stay active in the delivery flow. This is especially relevant for businesses handling frequent pickups and drops, where documentation issues can cause delays and increase operating costs, something operators try to avoid while planning routes and working to reduce logistics costs.
Yellow Plate vs White Plate Differences (India)
The most visible difference between private and commercial vehicle registration is the number plate colour, but the impact extends well beyond appearance.
A white number plate with black lettering is issued to privately registered vehicles. These vehicles are legally restricted to personal use and cannot be used for deliveries, passenger transport, or any income-generating activity. Even occasional paid deliveries using a white-plate vehicle are considered a violation.
A yellow number plate with black lettering is issued to commercially registered vehicles. It confirms that the vehicle is authorised to transport goods or passengers for business purposes. In 2026, traffic enforcement increasingly relies on number plate classification, FASTag data, and GPS activity to identify commercial usage on private registrations.
Using a white-plate vehicle for delivery work can result in fines, permit violations, vehicle seizure, and denial of insurance claims. To avoid these disruptions, delivery workflows, where orders are assigned, tracked, and completed through systems like MOVER, require vehicles to be commercially registered before they can operate without interruption.
Private Vehicle Registration vs Commercial Vehicle Registration: Side-by-Side Comparison
The comparison between private vehicle registration vs commercial vehicle registration clearly demonstrates why commercial vehicle registration for delivery is crucial in 2026, particularly for logistics and last-mile operations. Here’s a clear comparison to help you understand which registration type suits your use case:
|
Factor |
Private Vehicle Registration |
Commercial Vehicle Registration |
|
Purpose |
Personal use only |
Business & income generation |
|
Private number plates |
White plate, black letters |
Yellow plate, black letters |
|
Allowed for Delivery |
Not allowed |
Mandatory |
|
Road Tax |
Lower, usually one-time |
Higher, periodic slabs |
|
Insurance |
Private motor insurance |
Commercial vehicle insurance |
|
Fitness Certificate |
Not required |
Mandatory & periodic |
|
Permits |
Not required |
Goods/transport permit needed |
|
Legal Risk if Misused |
High (fines & rejection of claims) |
None if compliant |
Can a Private Vehicle Be Used for Delivery in India?
For years, the general rule in India was clear: private (white-plate) vehicles could not be used for commercial purposes such as deliveries or passenger transport. However, recent regulatory changes have introduced important exceptions, especially for two-wheelers.
What Has Changed in 2025?
In January 2025, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) issued the Motor Vehicle Aggregator Guidelines (MVAG) 2025, bringing long-awaited clarity to India’s shared mobility ecosystem.
Clause 23 of MVAG 2025: A Key Shift
As per Clause 23 of the MVAG 2025, state governments are now permitted to allow the use of non-transport (private) motorcycles for passenger rides through aggregator platforms such as bike-taxi services.
This means:
-
Private motorcycles can legally be used for passenger rides on aggregator platforms if the respective state government adopts and implements the guidelines.
-
Aggregators must comply with safety, insurance, onboarding, and regulatory requirements
-
States have the authority to set fees and additional conditions
-
This move has cleared the regulatory path for platforms like Rapido, Uber, and others, provided state approvals are in place.
Recent developments in cities like Bengaluru highlight how state-level implementation of vehicle-use rules plays a crucial role. While central guidelines under MVAG 2025 allow private motorcycles for passenger rides through aggregators, temporary suspensions and policy reversals at the state level have shown that permissions are not automatic or permanent.
This reinforces an important point for delivery partners and logistics operators: relying on regulatory exceptions is risky. For delivery and goods transport, commercial registration remains the most legally stable option across states, helping avoid sudden enforcement changes, fines, or operational disruptions.
What About Deliveries Using Private Vehicles?
It’s important to note that Clause 23 specifically applies to passenger rides on private motorcycles via aggregators. It does not automatically legalise the use of private vehicles for delivery purposes across India.
For deliveries:
-
Regulations continue to depend on state transport laws and enforcement practices.
-
Commercial usage may still require transport registration, appropriate insurance, and compliance approvals.
-
Businesses typically prefer legally compliant vehicles to avoid fines, insurance rejection, or operational disruptions.
Why Compliance Still Matters?
With increased enforcement through FASTag data, GPS tracking, and digital challans, non-compliant vehicle usage can lead to:
-
Heavy penalties
-
Rejected insurance claims
-
Vehicle seizure
-
Suspension of registration for repeat violations
This is why logistics and mobility platforms rely on legally permitted vehicles to ensure uninterrupted operations, reliable routing, and zero compliance risks.
Insurance Difference: Private vs Commercial Vehicles
Insurance is one of the biggest risk areas when choosing the wrong registration type. Private vehicle insurance covers personal usage only. The moment a private vehicle is used for delivery or commercial work, the policy becomes void. Even a minor accident during delivery can result in a rejected claim.
Commercial vehicle insurance, on the other hand, is designed for higher risk and daily usage. It covers:
-
Goods damage
-
Third-party liabilities
-
Delivery-related accidents
-
Business usage risks
For anyone planning to earn through deliveries or logistics, commercial insurance is not optional; it’s legally required and financially safer.
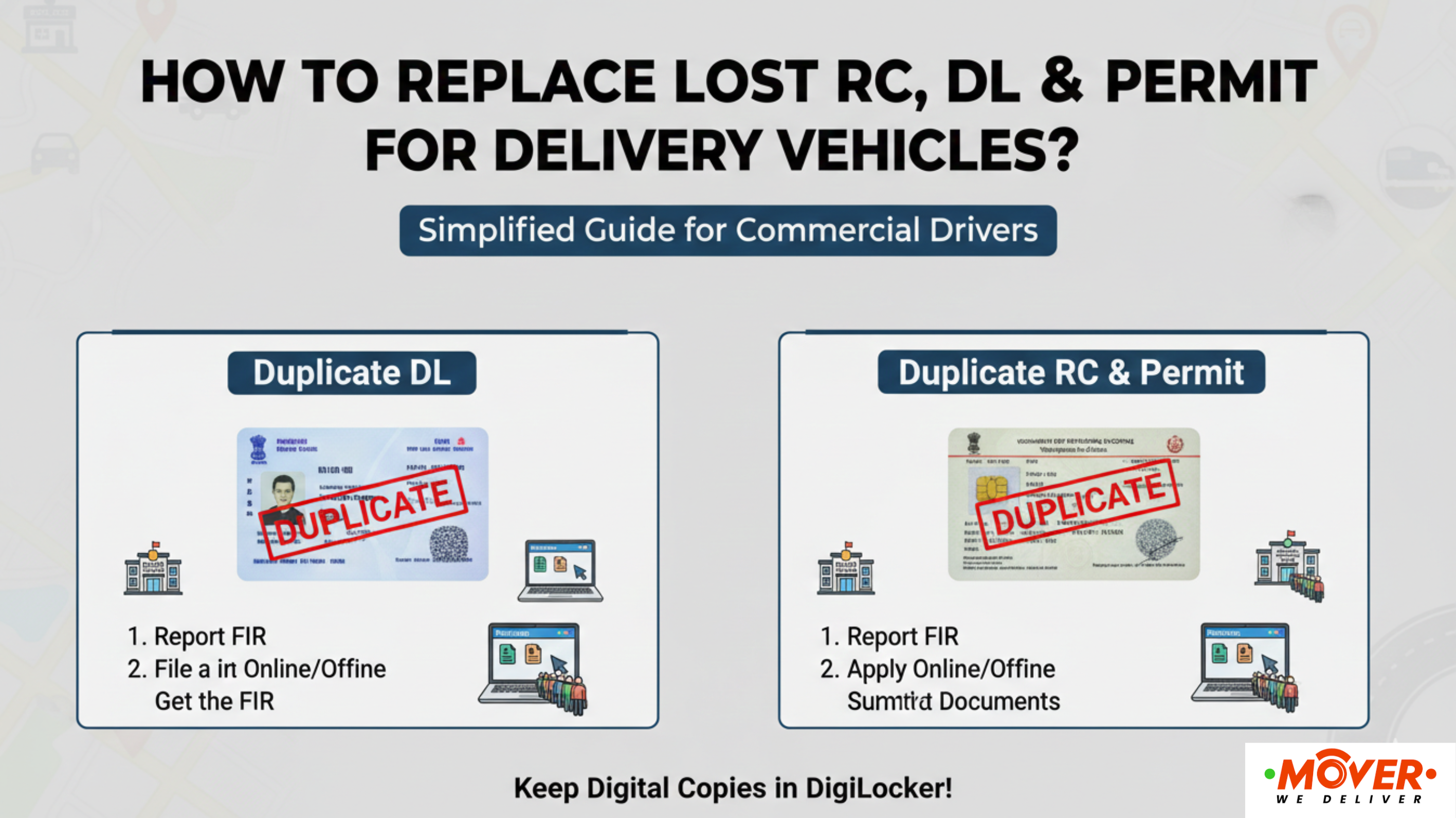
How to Convert a Private Vehicle to Commercial Registration?
If you plan to use your vehicle for deliveries or logistics, converting it from private to commercial registration is mandatory. The process is handled by the Regional Transport Office (RTO) and must be completed before starting delivery work.
Conversion Process Steps:
1. Clear existing hypothecation (if vehicle is on loan)
-
Obtain a No-Objection Certificate (NOC) from the financier
-
Complete hypothecation removal from RC
2. Gather required documents
-
Original RC (Registration Certificate)
-
Form 20 (Application for change of class of vehicle)
-
Form 30 (Notice of transfer of ownership - if applicable)
-
Valid insurance certificate
-
Proof of address
-
PAN card
-
Aadhar card
-
Passport-size photographs
3. Apply at RTO
-
Submit application with Form 20
-
Pay application fees (varies by state)
4. Update insurance
-
Cancel or let private insurance expire
-
Purchase a commercial vehicle insurance policy
-
Provide an insurance certificate to RTO
5. Pay tax differential
-
Calculate the difference between private and commercial road tax
-
Pay the differential amount (varies significantly by state and vehicle type)
6. Vehicle inspection
-
RTO conducts fitness inspection
-
The vehicle must meet commercial vehicle standards
-
Modifications may be required for compliance
7. Apply for permits
-
State goods permit for intra-state operations
-
National permit for inter-state operations (additional fees apply)
8. Receive new documents
-
Updated RC with commercial classification
-
New yellow number plate (or yellow-green for EVs)
Important Considerations:
-
Timeline: The entire process typically takes 2-4 weeks, though this varies by state and RTO workload.
-
Costs: Total costs include application fees, tax differential (major component), insurance premium increase, permit fees, and number plate costs. These vary dramatically by state, with the tax differential potentially ranging from ₹5,000 to ₹50,000+, depending on vehicle value and state.
-
Rejection scenarios: Applications may be rejected if the vehicle is too old (many states have age restrictions), doesn't meet fitness standards, or has pending challans.
-
State variations: Each state has slightly different procedures, forms, and fee structures. Check your specific state RTO website for exact requirements.
-
Loan implications: Some lenders may require notification or consent for registration type changes. This should be discussed with your financier.
Private vs Commercial Registration for Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles follow the same legal logic as petrol or diesel vehicles; the purpose of use decides the registration type.
-
A private electric vehicle (white plate or green-white plate) can only be used for personal travel.
-
An electric delivery bike or EV loader used for income must have commercial EV bike registration.
Commercial electric vehicles receive:
-
Green number plate with yellow lettering
-
Mandatory commercial insurance
-
Applicable EV permits (if required by city rules)
In 2026, enforcement for electric delivery bikes has increased, especially in metro cities. EVs used for logistics without proper commercial registration risk fines and suspension. Businesses focusing on logistics EV adoption prefer commercial EV fleets to ensure uninterrupted delivery operations.
Commercial Vehicle Registration for Delivery & Logistics Businesses
For delivery and logistics businesses, commercial vehicle registration is mandatory. Any vehicle used for last-mile delivery, courier work, or goods transport must be registered under the commercial category, regardless of size or fuel type.
With challenges like urban traffic impact on delivery, using a properly registered vehicle helps avoid delays caused by RTO checks, fines, or insurance disputes. Whether it’s bikes, electric goods loaders, or mini trucks operating from Transport Nagar hubs in India, every delivery vehicle needs a commercial RC, valid insurance, and permits.
In 2026, compliance checks rely heavily on VAHAN data, FASTag records, and fitness status. Organised delivery networks, including platforms like MOVER, depend on legally registered vehicles to ensure safe delivery in logistics and uninterrupted operations.
Why Commercial Registration Matters for Delivery & Logistics?
Using the correct registration type directly impacts:
-
Legal compliance
-
Insurance validity
-
Operational continuity
-
Platform onboarding
For example, delivery platforms and aggregators, including MOVER, only onboard vehicles with valid commercial vehicle registration for delivery. This ensures:
-
No route-level disruptions
-
No insurance rejections
-
Smooth intercity and intra-city movement
-
Compliance with RTO and traffic authorities
In 2026, digital enforcement systems easily flag private vehicles being misused for commercial purposes, making proper registration non-negotiable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Registering a Vehicle
Avoiding these mistakes saves money, prevents fines, and keeps delivery operations smooth. Many vehicle owners unknowingly make errors that lead to penalties:
-
Using a white-plate vehicle for paid deliveries
-
Buying commercial insurance without converting registration
-
Assuming electric bikes don’t need commercial registration
-
Skipping goods vehicle permits for delivery work
-
Registering under the wrong vehicle category
Final Verdict
The difference between private and commercial vehicle registration goes far beyond number plates. In 2026, vehicle usage defines legality. If a vehicle is used to earn money, even occasionally, it must be registered as a commercial vehicle.
For delivery partners, fleet owners, and logistics businesses, commercial registration provides legal protection, valid insurance coverage, and operational continuity. Delivery systems that manage order allocation, routing, and completion through MOVER depend on compliant vehicles to maintain uninterrupted movement and on-time execution.
In practical terms, choosing the correct registration type is not optional. It forms the foundation for safe, legal, and scalable delivery operations.
FAQs on Private Vehicle Registration vs Commercial Vehicle Registration
1. What is the main difference between private and commercial vehicle registration?
The key difference is usage. Private registration is for personal use only, while commercial registration allows the vehicle to earn income through deliveries or transport.
2. Is it legal to use a private vehicle for delivery in India?
Generally, using a private vehicle for delivery is not permitted under the Motor Vehicles Act without the proper permits. However, Clause 23 of the Motor Vehicle Aggregator Guidelines (MVAG) 2025 allows the use of non-transport (private) motorcycles for rides through aggregator platforms, as per state regulations.
3. What is the yellow plate vs white plate difference?
White plates are for private vehicles. Yellow plates indicate commercial vehicles authorised for goods or passenger transport. However, electric vehicles used for commercial purposes, such as car cabs or loading vehicles, have green plates with yellow lettering.
4. Can electric bikes be used for delivery without commercial registration?
No. Electric bikes used for delivery must have commercial registration with yellow-green number plates and commercial insurance, just like conventional delivery vehicles, regardless of being electric-powered.
5. Is commercial insurance mandatory for delivery vehicles?
Yes. Commercial insurance is legally required and covers delivery-related risks that private insurance does not.
6. What are private number plates in India?
Private number plates are white plates with black lettering issued to vehicles registered for personal use only. Vehicles with private number plates cannot legally be used for deliveries, courier services, or any income-generating activity in India.
7. What is the insurance difference between private and commercial vehicles?
The insurance difference between private vs commercial vehicles lies in usage coverage. Private insurance covers personal travel only, while commercial insurance covers delivery work, goods transport, third-party risks, and business-related accidents.